Statistical modeling of land ice changes in Antarctica and Greenland
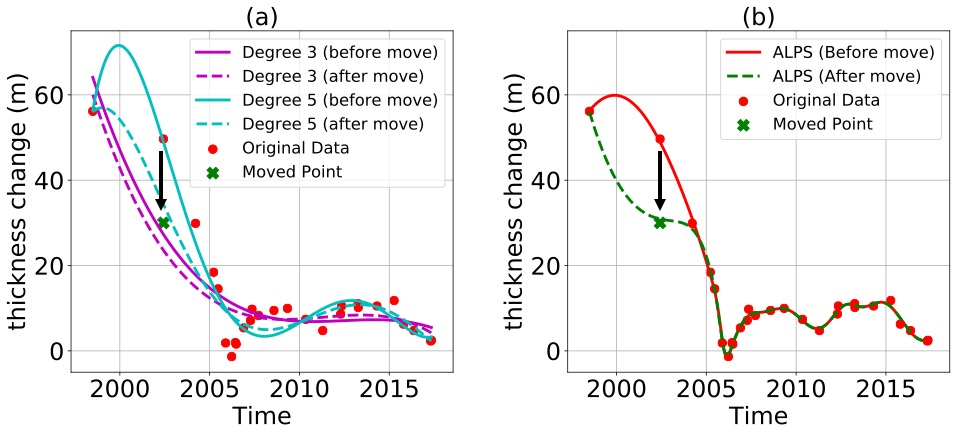 In this project spanning multiple years, we developed fast and efficient statistical methods to model spatio-temporal data from a variety of remote sensing instruments including multiple flight missions such as LVIS and ATM and satellite missions such as ICESat-2 and ICESat-1
In this project spanning multiple years, we developed fast and efficient statistical methods to model spatio-temporal data from a variety of remote sensing instruments including multiple flight missions such as LVIS and ATM and satellite missions such as ICESat-2 and ICESat-1
Relevant publications for this project
Shekhar P., Csathó B., Schenk T., Roberts C. and Patra A., ALPS: A Unified Framework for Modeling Time Series of Land Ice Changes. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing. 2020 Oct 16. Link arXiv Code.
Shekhar P., Csatho B., Schenk T. and Patra A., Localized time series modeling of Greenland ice sheet elevation changes. In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Climate Informatics: CI 2018 (No. NCAR/TN-550+PROC). doi:10.5065/D6BZ64XQ.
Shekhar P., Patra A. and Csatho B., Multiscale and Multiresolution methods for Sparse representation of Large datasets. Procedia Computer Science. 2017 Jan 1;108:1652-61Link.
Shekhar P. and Rai R., Anomaly Detection in Complex Spatiotemporal Networks Through Location Aware Geospatial Big Data Sets. In International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference 2016 Aug 21 (Vol. 50190). American Society of Mechanical Engineers Link.
Shekhar P., Patra A and Stefanescu ER., Multilevel methods for sparse representation of topographical data. Procedia Computer Science. 2016 Jan 1;80:887-96 Link.
